Changing position of services is also called roaming.
To locate an MS and to address the MS following number are required………..
Mobile station inter national ISDN number (MSISDN) :---------
The only important number for a user of GSM in is the phone number. Phone no is associated with SIM ,which is personalized for a user . This no consists of country code (CC) ,the national destination code(NDC) , and subscriber number (SN) .
International mobile subscriber identity(IMSI) :-------
GSM uses the IMSI for internal unique identification of a subscriber .it consists of mobile country code (MCC) ,the mobile network code(MNC) , and mobile subscriber identification identity(MSIN).
Temporary mobile subscriber identity(TMSI):
To hide the IMSI ,which would give the exact identity of the user signaling over the air interface ,GSM uses the 4 byte TMSI for local subscriber identification .TMSI is selected by the current VLR and is only valid temporarily and within the location area of VLR.
Mobile station roaming number(MSRN) :---Another temporary address that hides the location of a subscriber is MSRN. MSRN contains the current visitor country code(VCC) ,the visitor national destination code (VNDC)
The steps involve in calling from a fixed network to a MS (MTC) , and from a MS to fixed network(MOC) is given below…..
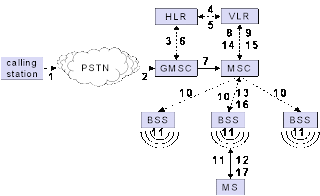
MOBILE TERMINATED CALL(MTC)
1: calling a GSM subscriber
2: forwarding call to GMSC
3: signal call setup to HLR
4, 5: request MSRN from VLR
6: forward responsible
MSC to GMSC
7: forward call to
current MSC
8, 9: get current status of MS
10, 11: paging of MS
12, 13: MS answers
14, 15: security checks
16, 17: set up connection
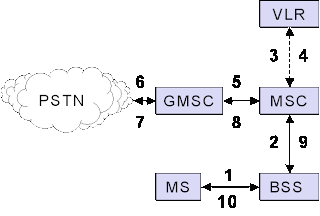
MOBILE OREGINATED CALL (MOC)
1, 2: connection request
3, 4: security check
5-8: check resources (free circuit)
9-10: set up call

MESSAGE FLOW FOR MTC AND MOC
No comments:
Post a Comment