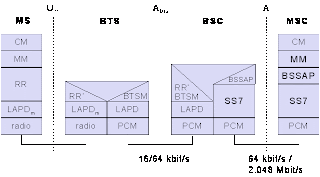
PROTOCOL ARCHITECTURE FOR SIGNALING
The main task of the physical layer comprise channel coding and error detection/correction . It uses different forward error correction (FEC) .
Physical layer contains special function such as voice activity detection(VAD),which transmits voice data only when there is a voice signal.
Signaling between entities in a GSM network requires higher layer . For this purpose the LAPDm protocol has been defined at Um interface for layer two. LAPDm has been derived from link access procedure for the D-channel in ISDN system ,which is a version of HDLC. LAPDm does not need synchronization flags or checksumming for error detection . LAPDm is also included segmentation and reassembly of data and acknowledged/ unacknowledged data transfer.
Third layer in GSM system is network layer .The lowest sublayer is the radio resource management(RR) , is implemented in the BTS and remainder is situated in the BSC .The main task of RR are setup ,maintenance ,and release of radio channels . RR also directly access the physical layer for radio information and offers a reliable connection to next higher layer. Mobility management (MM) contains functions for registration , location updating ,identification and provision of a temporary mobile
subscriber identity(TMSI) that replace the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) .The call management(CM) layer contains three entities : call control(CC) , short message service(SMS) , and supplementary services(SS) .SMS allows for message transfer using protocol channels SDCCH and SACCH. This layer also provides functions to send in-band tones , called dual tone multiple frequency (DTMF). Data transmission at the physical layer uses pulse code modulation (PCM) .
PCM system offer transparent 64 kbps channels, GSM allows for submultiplexing of four 16kbps channels into a single 64 kbps. The physical layer at the A interface typically includes leased lines with 2.048 Mbps capacity. LAPD is used for layer two at Abis ,BTSM for BTS management.
Signaling System No.7(SS7) is used for signaling between an MSC and a BSC. This protocol also transfer all management information between MSCs , HLR , VLRs , AuC , EIR and OMC. An MSC can also control a BSS via a BSS application part (BSSAP) .
No comments:
Post a Comment