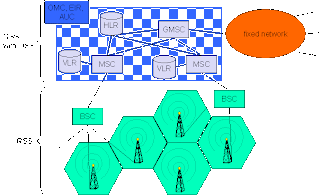
GSM comes with hierarchical, complex system architecture containing many entities, acronyms and interfaces. GSM consists of three-sub system…
1. Radio Subsystem (RSS)
2. Network and switching subsystem(NSS)
3. Operation subsystem(OSS)
RADIO SUBSYSTEM
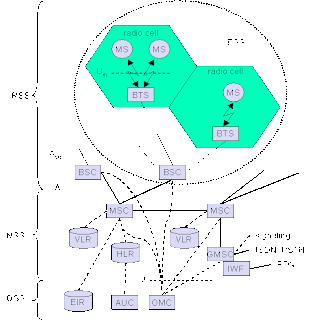
The RSS comprise all radio specific entities like MS and base station subsystem (BSS) .The RSS connected with NSS via A interface and NSS connected with OSS via O interface. The A interface is typically based on circuit-switched PCM-30 system carrying up to 30-64 kbit/s connection and O interface uses the Signaling System no.7 based on X.25 carrying management data to/from the RSS. The component of RSS are given below…
Base station subsystem (BSS)
A GSM network comprise many BSS, each controlled by a BSC .The BSS perform all function necessary to maintain radio connection to MS, coding/decoding of voice and rate adaptation to/ from the wireless network part. BSS contains several BTS.
¨Base transceiver station (BTS)
A BTS comprise all radio equipment i.e. antenna, signal processing, amplifiers
Necessary for the radio transmission BTS can form a radio cell or, usage sectored antenna several cells and is connected to MS via Um interface, and to the BSC via the ABIOS interface.
¨Base station controller (BSC)
The BSC basically manages the BTS .It receives radio frequencies, handle handover from one BTS to another within the BSS and performs paging of the MS.The BSC also multiplexes the radio channels onto the fixed network at the A interface.
¨ MOBILE STATION (MS)
Mobile station comprises all user needed software and hardware for the communication using gsm services.MS consists of a SUBSCRIBER IDENTITY MODULE(SIM) which stores all user data relevant to the gsm.ms can be identified with its international mobile equipment identity(IMEI) for the theft protection. Without the sim only the emergency calls are posible.SIM contains ……
1.personel identity no.(PIN)
2.PIN unblocking key(PUK).
3.Authentication key ki.
4.International mobile subscribers identity(IMSI)
The pin is used to unlock the MS. Using the wrong pin three times will lock the SIM.
The MS stores the dynamic information e.g. cipher key Kc ,temporary mobile subscriber identity (TMSI) and location area identification(LAI).It consists of three part ……
1. Mobile terminal(MT)
2. Terminal adapter(TA)
3. Terminal equipment(TE)
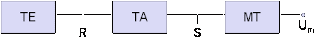



NETWORK AND SWITCHING SUBSYSTEM
The brain of GSM is formed by NSS. The NSS connects the wireless network with standard public network, performs handover between different BSS, and comprises function for worldwide location of users and supports charging, accounting, and roaming of users between different providers in different countries. The NSS consists of the following components…
Mobile services switching center (MSC): --
MSCs are high performance digital ISDN switches. They set up connections to other MSCs and to the BSCs via A interface and form the fixed backbone network of GSM system . A gateway MSC (GMSC) has additional connections to other fixed networks e.g. ISDN and PSTN. Using additional interworking functions (IWF), an MSC can also connect to public data networks (PDN) such as X.25. An MSC handles all signaling needed for connection setup, connection release and handover connections to other MSCs. The standard signaling system NO. 7(SS7) is used for this purpose.
¨HOME LOCATION REGISTER (HLR): --
The HLR is most important database in a GSM network system and store all static user relevant information like mobile subscriber ISDN number (MSISDN), subscriber services e.g. call forwarding, roaming restrictions, GPRS and inter mobile subscriber identity (IMSI). It also contains dynamic information such as current location area (LA) of the MS, the mobile subscriber roaming number (MSRN), and current VLR and MSC.
¨VISITOR LOCATION REGISTER (VLR): --
The VLR associated each MSC is a dynamic data base which stores all important information needed for the MS users currently in the la served by the MSC.If a new MS comes in to the LA the VLR is responsible to deal with it. Some VLRs in existence are capable of storing one million customers.
OPERATION SUBSYSTEM (OSS): --
It contains the necessary functions of network operation and maintenance.it contains the network entities of its own and accesses others from SS7 protocol. The following entities have been defined..
¨OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE CENTRE (OMC):
The OMC contains and monitors all other network entities via the o interface. OMCs use the telecommunication management network(TMN).
It manages traffic monitoring ,status reports of network entities, subscriber and security management or accounting and billing.
Authentication center (AuC):---
A AuC is defined to protect user identity and data transmission. The AuC contains algorithm for authentication as well as the key for encryption and generate the value needed for user authentication in the HLR.
Equipment identity register(EIR):---
The EIR is a database for all IMEIs and stores all device identification registered for this system. The EIR has a white list for valid MS and blacklist for stolen MS.A MS is useless as soon as the owner has reported a theft.
No comments:
Post a Comment