GSM 900 is divided into 124 channels ,each 200khz wide using FDMA. Channel 1 and channel 124 is not used for transmission , 32 channels are reserved for organizational data and remaining 90 channels are used for voice transmission. Each 200 khz carrier is subdivided into frames that repeated continuously. The duration of a frame is 4.615 ms .A frame is subdivided into 8 GSM time slots with a duration of 577 ms .
Data is transmitted in small portions called burst .The burst is only 546.5 ms long and contains 148 bits .The remaining 30.5 ms is used as guard space to avoid overlapping with other bursts due to different path delays and give the transmitter time to turn on and off. The physical channel has a raw data rate of about 33.8kbps,each radio carrier transmitted approximately 270 kbps over Um interface .THE FIRST and last A three bits of a normal burst are all set to zero and can be used to enhance the receiver performance .the training sequence in the middle of a slot is used to adapt the parameter of the receiver to the current path propagation and select the strongest signal in case of multi path propagation. A flag S indicates where the data field contains user or network control data .A frequency correction burst allows the MS to correct the local oscillator to avoid interference with neighboring channels . synchronization burst with an extended training sequence synchronizes the MS with the BTS in time ,an access burst is used for the initial correction setup between MS and BTS an finally a dummy burst is used if no data is available for a slot .
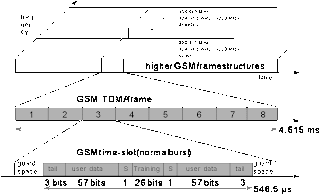
GSM TDMA FRAME SLOTS, AND BURSTS
No comments:
Post a Comment